

![]()
This backend dynamically enabeles the options that are supported by the scanner in dependence of the scanning-mode and other options. Here is an example of the frontend xsane :

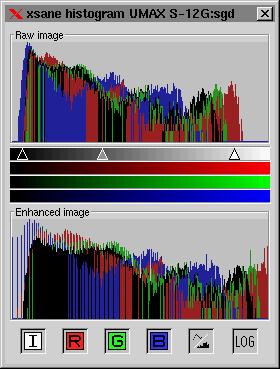
The options Gamma, brightness, contrast and negative in the main window come from xsane that calculates a gamma table using this values. These values are corelated to highlight, midlight and shadow sliders in the Histogram window.
| Mode | Remark |
| Lineart | 1 bit/pixel black/white mode |
| Halftone | 1 bit/pixel dithered black/white mode |
| Grayscale | 8 / 9 / 10 / 12 / 14 / 16 bits/pixel gray mode |
| Color | 24 / 27 / 30 / 36 / 42 / 48 bits/pixel RGB mode |
| Scan sources |
| Flatbed |
| Transparency adapter (UTA) |
| Automatic document feeder (ADF) |

| Standard options | Remark |
| Analog gamma correction | Define the value for analog gamma correction. *
Value between 1.0 and 2.0 . (Analog gamma correction doesn't reduce the number of used colors) |
| Highlight | Define the intensity that shall be considered white. * |
| Shadow | Define the intensity that shall be considered black. * |
| Contrast | Define the contrast of the image - only available in halftone-mode. |
| Brightness | Define the brightness of the image - only available in halftone-mode. |
| Threshold | Define the minimum intensity to get a white point- only available in lineart-mode. |
| Use custom gamma table | Use free definable scanner internal digital gamma table.
If you enable this option, the gamma correction is done inside the scanner. If you have a scanner with more than 8/24 bits/pixel, the image is scanned with the maximum available bit depth. The gamma correction does transform the image form the internal bit depth to the selected output bit depth (see below). The frontends do handle the usage of the gamma table different. If you use xsane, you should enable this option to use the maximum available bit depth (otherwise xsane does the conversion with the selected output bit depth). (Side-effect: digital gamma correction may reduce the number of used colors -especally if the used bit depth is low.) |
| Quality calibration | Use quality white calibration. * |
| Double optical resolution | Use lens 2 on high end scanners, this reduces the scanwidth and increases the maximum scanresolution. * |
| Negative scan | Inverts color intensity - for scanning negatives. |
| Bit depth | Image depth in bits/sample the scanner sends to the computer, normally
8 in grayscale and color mode. Some scanners support more than 8bits/sample,
but only few file formats support it. If your scanner supports more than
8bis/sample you already get an improvement if you set the bit detpth to
8 and enable the option use custom gamma table (see above) because
the scanner internal gamma correction is done with the maximum available
bit depth!!!
|
| Lamp warmup | Enable extended lamp-warmup. * |
* only available for some scanners

| Advanced options | Remark |
| Set exposure time | Enable selection of exposure time, if not enabled, scanner uses default values. * |
| Cal. exposure time | Define exposure time for calibration. * |
| Scan exposure time | Define exposure time for scan. * |
| Set lamp density | Enable selection of lamp density, if not enabled, scanner automatically selects a value. * |
| Cal. lamp density | Define lamp density for calibration. * |
| Set scan lamp density | Enable selection of lamp density for scan, if not enabled scanner uses the value that was used for calibration. * |
| Scan lamp density | Define lamp density for scan. * |
| lamp on | Turn on scanner lamp. * |
| lamp off | Turn off scanner lamp. * |
| lamp off at exit | Turn off scanner lamp when program exits (when sane_close is called) * |
* only available for some scanners