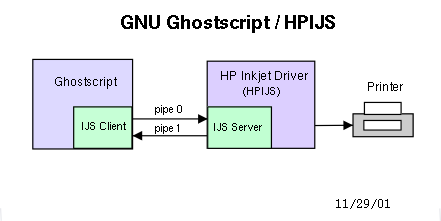
There are two parts to the IJS interface - IJS client that resides in GNU Ghostscript and the IJS server. The IJS server is built into the printer driver, in our case the HP Inkjet driver. In this document the term IJS server, HPIJS server, HPIJS, or HP Inkjet Driver are all synonymous. They all refer to the same software component. HPIJS runs as a server or co-process to GNU Ghostscript. The server is spawned automatically by GNU Ghostscript. The following figure is a high level overview of the IJS interface between GNU Ghostscript and HPIJS.

GNU Ghostscript is a software application that interprets PostScript and displays the results on the screen or converts the PostScript into a form you can print on a non-PostScript printer.
PostScript is a programming language optimized for printing graphics and text, it is sometimes called a page description language. Most Linux applications support PostScript. Postscript is the standard for printing in any Linux or Unix environment.
Ghostscript supports many output devices, including many different printers. This document addresses how to build, install and use HPIJS with Ghostscript. This document is intended for distributions and experienced users. Other users should refer to their appropriate Linux distribution for HPIJS support.
Although HPIJS runs as a separate process from Ghostscript, HPIJS still looks like just another Ghostscript printer driver. Adding printer drivers is a well documented interface that is described in the GNU Ghostscript documentation at http://www.cs.wisc.edu/~ghost/doc/gnu/index.htm. Together with Ghostscript and HPIJS, PostScript can be converted to a printer language that is compatible with many of the latest HP inkjet products. See Installation on how to download and install HPIJS.
This version of HPIJS supports both the new IJS interface and the old HPIJS interface. Support for the HPIJS interface is provided for backward compatibility only. Most new features will be supported on the IJS interface only. The HPIJS interface is defined in the HPIJS 0.97 release. Information on the IJS interface can be found at inkjet-list.
Ghostscript is not a gui application. Ghostscript is a command line application that runs from a Linux shell, similar to a Microsoft DOS command run from a DOS window.
Ghostscript can be used by itself to print to a non-Postscript printer, but generally a print spooler must be used. The print spooler must be configured to use Ghostscript when printing to a non-Postscript printer. Many Linux distributions all ready support HPIJS in their spooler system, see their web site for spooler support questions. Additional information is available at www.linuxprinting.org.
HPIJS is platform-independent and works on many different Unix and Linux systems. In order to install HPIJS the download includes an automake/autoconf makefile. This portable build procedure requires an ANSI C compiler, ANSI C++ compiler and a POSIX compliant environment.
This version of HPIJS supports both the new IJS interface and the old HPIJS interface. HPIJS requires Ghostscript to support one of these two interfaces.
Many platforms (Red Hat, Mandrake, SuSE, Yellow Dog, FreeBSD, Debian, HPUX, AIX, etc) have been confirmed to work, please see those sites for more information.
HPIJS supports all the current HP printer models with different Ghostscript command line parameters. Different printer models can be selected with the IEEE 1284 Manufacturer and Model strings. This information can come from the query of a printer over the parallel or usb port.
The following Ghostscript commands are required when using HPIJS.
-sDEVICE=ijs -sIjsServer=hpijs -dIjsUseOutputFD -sDeviceManufacturer=x (x equals: "HEWLETT-PACKARD", "APOLLO") -sDeviceModel=x (x equals: "DESKJET 990", "DESKJET 670", etc...)The following Ghostscript commands are optional when using HPIJS.
-dDuplex=false -dTumble=false (none)
-dDuplex=true -dTumble=false (book)
-dDuplex=true -dTumble=true (tablet)
-sIjsParams="Quality:Quality=n,Quality:ColorMode=n,Quality:MediaType=n,Quality:PenSet=n,Quality:FullBleed=n"
Quality equals: 0=normal (default), 1=draft, 2=best, 3=hires
ColorMode equals: 0=grey_k, 1=grey_cmy, 2=color (default)
MediaType equals: 0=plain (default), 1=premium, 2=photo
PenSet equals: 0=black_pen, 1=color_pen, 2=both_pens, 3=mdl_pen, 4=mdl_both
FullBleed equals: 0=no (default), 1=yes
PenSet Definitions
black_pen: only black pen in the printer color_pen: only color pen in the printer both_pens: black & color pens in printer mdl_pen: photo pen in the printer mdl_both: color pin and photo pen in printerNote, there are defaults for all optional commands. PenSet default is defined by each device class.
The Quality, MediaType, ColorMode, PenSet and FullBleed are used to set the print mode. Not all combinations of Quality, MediaType, ColorMode, PenSet and FullBleed are valid print modes. If an invalid print mode is set, the job will still print, because HPIJS will default to a print mode that makes sense given the input. HPIJS will send any error message to stderr and syslog. Print modes are device class specific, see the following device descriptions for more details.
The following devices classes are currently supported by HPIJS. Each device class lists the DeviceModel parameter associated with that class. Each device class support 300x300dpi unless specified otherwise.
Draft Grayscale
Quality=1 ColorMode=0 MediaType=0 PenSet=0
Draft Color
Quality=1 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=1
Normal Grayscale
Quality=0 ColorMode=0 MediaType=0 PenSet=0
Normal Color (default)
Quality=0 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=1
Draft Grayscale
Quality=1 ColorMode=0 MediaType=0 PenSet=0
Draft Color
Quality=1 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=1
Quality=1 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Normal Grayscale
Quality=0 ColorMode=0 MediaType=0 PenSet=0
Normal Color
Quality=0 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=1 (default)
Quality=0 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Photo
Quality=2 ColorMode=2 MediaType=1 PenSet=4
Draft Grayscale
Quality=1 ColorMode=0 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Draft Color
Quality=1 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Normal Grayscale
Quality=0 ColorMode=0 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Normal Color (default)
Quality=0 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Draft Grayscale
Quality=1 ColorMode=0 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Draft Color
Quality=1 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Normal Grayscale
Quality=0 ColorMode=0 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Normal Color (default)
Quality=0 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Photo
Quality=2 ColorMode=2 MediaType=1 PenSet=4
Draft Grayscale
Quality=1 ColorMode=0 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Draft Color
Quality=1 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Normal Grayscale
Quality=0 ColorMode=0 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Normal Color (default)
Quality=0 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Photo
Quality=2 ColorMode=2 MediaType=2 PenSet=2
Draft Grayscale
Quality=1 ColorMode=0 MediaType=0 PenSet=1
Draft Color
Quality=1 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=1
Quality=1 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Normal Grayscale
Quality=0 ColorMode=0 MediaType=0 PenSet=1
Normal Color
Quality=0 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=1 (default)
Quality=0 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Photo
Quality=2 ColorMode=2 MediaType=2 PenSet=1
Quality=2 ColorMode=2 MediaType=2 PenSet=2
Draft Grayscale
Quality=1 ColorMode=0 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Draft Color
Quality=1 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Normal Grayscale
Quality=0 ColorMode=0 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Normal Color (default)
Quality=0 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Photo
Quality=2 ColorMode=2 MediaType=2 PenSet=2
Draft Grayscale
Quality=1 ColorMode=0 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Draft Color
Quality=1 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Normal Grayscale
Quality=0 ColorMode=0 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Normal Color (default)
Quality=0 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
HiRes
Quality=3 ColorMode=2 MediaType=2 PenSet=2
Draft Grayscale
Quality=1 ColorMode=0 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Draft Color
Quality=1 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=1
Quality=1 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Normal Grayscale
Quality=0 ColorMode=0 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Normal Color
Quality=0 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=1 (default)
Quality=0 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Photo
Quality=2 ColorMode=2 MediaType=1 PenSet=4
Draft Grayscale
Quality=1 ColorMode=0 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Draft Color
Quality=1 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=1
Quality=1 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Normal Grayscale
Quality=0 ColorMode=0 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Normal Color
Quality=0 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=1 (default)
Quality=0 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Photo
Quality=2 ColorMode=2 MediaType=1 PenSet=4
Draft Grayscale
Quality=1 ColorMode=0 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Draft Color
Quality=1 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=1
Quality=1 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Normal Grayscale
Quality=0 ColorMode=0 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Normal Color
Quality=0 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=1 (default)
Quality=0 ColorMode=2 MediaType=0 PenSet=2
Photo
Quality=2 ColorMode=2 MediaType=1 PenSet=4
Normal (default)
Quality=0,ColorMode=2,MediaType=0,PenSet=1,FullBleed=1
HiRes
Quality=3,ColorMode=2,MediaType=2,PenSet=1,FullBleed=1
For example, a Device ID query on a Deskjet 990Cxi will return "DESKJET 990C". If DeviceModel="DESKJET 990C", HPIJS will match to "DESKJET 99", ignore the "0C" and select the DJ9xxVIP device class. See models.cpp for a list of all model strings and how they are wild-carded.
inches: postscript units:
1. Letter 8.5 x 11 612 x 792
2. Legal 8.5 x 14 612 x 1008
3. Ledger 11 x 17 792 x 1224
4. Executive 7.25 x 10.5 522 x 756
5. A3 11.69 x 16.53 842 x 1190
6. A4 8.27 x 11.69 595 x 842
7. A5 5.83 x 8.27 420 x 595
8. A6 4.13 x 5.83 297 x 420
9. Photo 4 x 6 288 x 432
10. B4 10.126 x 14.342 729 x 1033
11. B5 7.17 x 10.126 516 x 729
12. Oufuku-Hagaki 5.83 x 7.87 420 x 567
13. Hagaki 3.94 x 5.83 284 x 420
14. Super B 13 x 19 936 x 1368
15. Flsa 8.5 x 13 612 x 936
1. Added new printer support for Business Inkjet 2200/2230/2250/2280. 2. Added HiRes mode to the PS100 device class. 3. Added Draft modes to most device classes. 4. Bumped DJ8xx and DJ8x5 Normal Grayscale support to 600 dpi. 5. Added support for paper sizes Ledger, Executive, Super B and Flsa.This release fixes a DJ9xxVIP duplex problem with GNU Ghostscript 7.05 and HPIJS 1.0.4. The problem caused the second page to print incorrectly when duplex was enabled. The problem occurred with 300 dpi input not 600 dpi input.
1. Added a new HiRes mode to DJ9xxVIP device class. 2. Added support for paper sizes A3 and A5. 3. Removed Photo Full Bleed paper size and added a FullBleed parameter. 4. Fixed a duplex top margin problem with paper sizes other than Letter. 5. Fixed a duplex top margin problem with grey_k and grey_cmy. 6. Fixed a problem detecting B4 and B5 paper sizes. 7. Fixed a artifact (black vertical line) that could occur in the right margin.The new HiRes mode supports the maximum resolution for DJ9xxVIP device class. For these devices the box specification for resolution is 2400x1200. In the past no scaling was done to 2400 in the printer.
Full bleed support is no longer a separate paper size. Full bleed is enabled with a new Ghostscript command called FullBleed. Now you just select your 4x6 paper size and set FullBleed=1.
This release is compatible with IJS 0.33. In order to be compliant with IJS 0.33, some Ghostscript commands have changed from HPIJS 1.0.2.
The Duplex command has changed from -dDuplex=n (n equals: 0=none, 1=tablet, 2=book) to following.
-dDuplex=false -dTumble=false (none) -dDuplex=true -dTumble=false (book) -dDuplex=true -dTumble=true (tablet)HPIJS print mode parameters must use the "Quality:" prefix. The prefix will allow better management of parameter namespace. See the following Ghostscript command example.
-sIjsParams="Quality:Quality=0,Quality:ColorMode=2,Quality:MediaType=0,Quality:PenSet=2"The following Ghostscript command without the "Quality:" prefex is no longer supported.
-sIjsParams="Quality=0,ColorMode=2,MediaType=0,PenSet=2"The new Ghostscript command -dIjsUseOutputFD is required when using HPIJS.
1. Fixed a problem printing Photo Full Bleed on the Photosmart 100. 2. Cleaned up BSD documentation in source files.
1. Fixed a setpagedevice problem with the IJS client. PageSize can now be set from postscript. 2. Fixed a off-by-one error in IJS server, gcc -O2 optimization now seems to work. 3. Updated the documentation, see the hpijs_readme.html file.
Deskjet 656 Photosmart 100 Apollo P-22 Deskjet 825/845 Photosmart 1115 Apollo P2500 Deskjet 920 Photosmart 1215 Apollo P2600 Deskjet 940/948 Photosmart 1315 Deskjet 995 CP 1160 Deskjet 1125 CP 1700 Deskjet 1220 Deskjet 2250Added support for the IJS interface. This release is backward compatible with HPIJS 0.97 interface.
Added support for Duplex. Duplex is only available with the IJS interface. When Duplex mode is set, top and bottom margins are set to 1/2 inch.
Added support for the following paper sizes. The new paper sizes are only available with the IJS interface.
Photo, Photo Full Bleed, A6, B4, B5, Oufuku-Hagaki, HagakiThe PrintMode command has been replaced with separate commands - Quality, ColorMode, MediaType and PenSet. These commands are only available with the IJS interface.
Changed top margin from 1/3 to 1/8 inch. Also, changed the bottom margin to 1/2 inch. Note, on the 6xx series the maximum bottom margin is .46 inch for black and .587 for color. This means for the 6xx series, color printing to within 1/2 inch bottom margin is not guaranteed.
Added a platform-independent automake/autoconf makefile.
This update fixes some of the following problems.
1. A line of text near the top of the page would not print. 2. Top and bottom margins on multiple page jobs was not consistent.
DeskJet980 DeskJet960 DeskJet350 Photosmart 1000/1100 Photosmart 1215/1218
Made a small change to the top and right margins in gdevhpij.c. This corrects a problem where both Ghostscript and HPIJS were trying to set the margins.
Added some query commands to the GS/HPIJS communication interface. These commands can be used to return current printer parameters.
This release is backward compatible with HPIJS 0.95.
Changed Ghostscript command interface to HPIJS driver. The HPIJS driver is now called with the following Ghostscript commands.
-sDEVICE=hpijs
-sDeviceName=x
where x equals: DJ630, DJ6xx, DJ6xxPhoto, DJ8xx, DJ9xx or DJ9xxVIP
This removes the hard coded device parameters from gdevhpij.c so new printer
drivers can be added to HPIJS with out re-compiling Ghostscript.
The old interface used the following Ghostscript commands.
-sDEVICE=x
where x equals: DJ630, DJ6xx, DJ6xxP, DJ8xx, DJ9xx or DJ9xxVIP
The old interface is degraded and will eventually be dropped. New printer
drivers will not use the old interface.
This section includes instructions for compiling Ghostscript from source code, but this is not an easy task. Before attempting to update Ghostscript, check with your distribution, they may have a Ghostscript update with the latest HPIJS support.
This section does not address how to update your spooler or how to use HPIJS with your spooler. See your distribution about spooler questions. Additional information is available at www.linuxprinting.org.
# tar xzvf hpijs-1.0.tar.gz # cd hpijs-1.0 # ./configure # make # make installYou can verify HPIJS was build and installed correctly with the following command.
# hpijs -h Hewlett-Packard Co. Inkjet Server 1.0 Copyright (c) 2001, Hewlett-Packard Co.This is all you need to do to install HPIJS. If your current Ghostscript supports the IJS or HPIJS interface you are done. If you are not sure the Ghostscript Install section will show you how to verify IJS or HPIJS interface support.
Your current Ghostscript may already support HPIJS. You can verify this with the gs -h command. You should see output similar to this.
GNU Ghostscript 6.53 (2002-02-13) Copyright (C) 2002 artofcode LLC, Benicia, CA. All rights reserved. Usage: gs [switches] [file1.ps file2.ps ...] Most frequently used switches: (you can use # in place of =) -dNOPAUSE no pause after page | -q `quiet', fewer messages -gIf you don't see any of the above highlighted devices your version of Ghostscript does not have built-in support for HPIJS.x page size in pixels | -r pixels/inch resolution -sDEVICE= select device | -dBATCH exit after last file -sOutputFile= select output file: - for stdout, |command for pipe, embed %d or %ld for page # Input formats: PostScript PostScriptLevel1 PostScriptLevel2 PDF Available devices: x11 bbox x11alpha x11cmyk x11gray2 x11gray4 x11mono bmpmono bmpgray bmpsep1 bmpsep8 bmp16 bmp256 bmp16m bmp32b deskjet djet500 laserjet ljetplus ljet2p ljet3 ljet3d ljet4 ljet4d lj5mono lj5gray cdeskjet cdjcolor cdjmono cdj550 pj pjxl pjxl300 uniprint ijs hpijs DJ630 DJ6xx DJ6xxP DJ8xx DJ9xx DJ9xxVIP AP21xx bj10e bj200 bjc600 bjc800 faxg3 faxg32d faxg4 pcxmono pcxgray pcx16 pcx256 pcx24b pcxcmyk pbm pbmraw pgm pgmraw pgnm pgnmraw pnm pnmraw ppm ppmraw pkm pkmraw pksm pksmraw tiffcrle tiffg3 tiffg32d tiffg4 tifflzw tiffpack tiff12nc tiff24nc psmono psgray psrgb bit bitrgb bitcmyk png16m pnggray pngmono png256 png16 jpeg jpeggray pdfwrite pswrite epswrite pxlmono pxlcolor cljet5 cljet5c nullpage Search path: . : /usr/share/ghostscript/6.53/lib : /usr/share/ghostscript/fonts For more information, see /usr/share/ghostscript/6.53/doc/Use.htm. Report bugs to bug-gs@ghostscript.com, using the form in Bug-form.htm.
The ijs device supports the IJS interface. All other devices (hpijs DJ630 DJ6xx DJ6xxP DJ8xx DJ9xx DJ9xxVIP AP21xx) are supported through the old HPIJS interface. Both interfaces are supported by HPIJS, but the IJS interface replaces the old HPIJS interface.
If Ghostscipt does not support HPIJS, check with your distribution and see if they have a Ghostsript update.
If necessary, the following instructions show you how to build GNU Ghostscipt 6.53. GNU Ghostscript 6.53 or higher will have built-in support for the IJS interface.
../gs6.53/ ../gs6.53/jpeg/ ../gs6.53/libpng/ ../gs6.53/zlib/
# ln -s /usr/share/fonts/default/Type1 /usr/share/ghostscript/fonts
# ./configure prefix=/usr # make # make install
StartEntry: IJS
GSDriver: ijs
Description: {IJS Client}
About: { \
This is a generalized IJS client interface for ghostscript printer \
drivers. Different drivers and options are specified in the \
"Extra GS options" box. The following ghostscript commands are used by the \
HP Inkjet Driver (HPIJS): -sIjsServer=hpijs, \
-sDeviceManufacturer="HEWLETT-PACKARD", \
-dIjsUseOutputFD, -sDeviceModel=model, -dDuplex, -dTumble, -sIjsParams=options. \
Where DeviceModel equals one of the following: "DESKJET 990", "DESKJET 970", etc... \
-dDuplex equals book, -dDuplex -dTumble equals tablet. \
IjsParams can be any of the following: Quality=n, MediaType=n, ColorMode=n, PenSet=n. \
Where Quality equals one of the following: 0=normal (default), 1=draft, 2=best. \
MediaType equals one of the following: 0=plain (default), 1=premium, 2=photo. \
ColorMode equals one of the following: 0=grey_k, 1=grey_cmy, 2=color (default). \
PenSet equals one of the following: 0=black_pen, 1=color_pen, 2=both_pens, \
3=mdl_pen, 4=mdl_both. \
Not all combinations of Quality, MediaType and ColorMode are valid print modes. \
Resolution setting 600x600 is available for some print modes only. \
In printtool special characters must be preceded by a double backslash see the \
following example for HP 990C: -sIjsServer=hpijs -sDeviceManufacturer=\\"HEWLETT-PACKARD\\" \
-dIjsUseOutputFD -sDeviceModel=\\"DESKJET 990C\\". \
}
Resolution: {300} {300} {}
Resolution: {600} {600} {}
EndEntry
In PrintTool special characters must be preceded by a double backslash (see example above).
Note, PrintTool has a problem with double backslash.
PrintTool allows you to set double backslash, but it will only read one backslash back when editing.
This means if you are editing the Extra GS options you must re-enter the double backslash.
$ lpr -Plp0 tiger.ps
Most applications use the lpr command to print documents.
$ gs -sDEVICE=ijs -sIjsServer=hpijs -dIjsUseOutputFD -sDeviceManufacturer="HEWLETT-PACKARD" -sDeviceModel="DESKJET 990" -r300 -dNOPAUSE -dSAFER -sOutputFile="/dev/lp0" file.ps -c quitThis command line example shows how to print a 4x6 inch photo from a digital camera.
$ convert -rotate 90 p8160010.jpg p8160010.png $ convert -page 324x432-18+0 p8160010.png photo.ps $ gs -sDEVICE=ijs -sIjsServer=hpijs -dIjsUseOutputFD -sDeviceManufacturer="HEWLETT-PACKARD" -sDeviceModel="DESKJET 990" -r300 -dNOPAUSE -dSAFER -sOutputFile="/dev/lp0" -dDEVICEWIDTHPOINTS=288 -dDEVICEHEIGHTPOINTS=432 photo.ps -c quitThe first command rotates the picture 90 degrees and converts from jpg to png. The second command converts the png to postscript and scales the image to 4.5x6 inches. The original photo was 1280x960 pixels. In order to keep the same aspect ratio as the original photo, the second command scales to 4.5x6 instead of 4x6 inches. The means we need to clip the top and bottom (x axis) by 0.25 inches. Ghostscript parameters DEVICEWIDTHPOINTS=288 and DEVICEHEIGHTPOINTS=432 specify the actual paper size in postscript units, which in this case represents 4x6 inches (288=4*72, 432=6*72).
Similar to the above example, here is a 4x6 full bleed (borderless) photo printing example using the Photosmart 100.
$ convert -rotate 90 p8160010.jpg p8160010.png $ convert -page 324x432-18+0 p8160010.png photo.ps $ gs -sDEVICE=ijs -sIjsServer=hpijs -dIjsUseOutputFD -sDeviceManufacturer="HEWLETT-PACKARD" -sDeviceModel="PHOTOSMART 100" -r600 -sIjsParams="Quality:FullBleed=1" -dNOPAUSE -dSAFER -sOutputFile="/dev/usb/lp0" -dDEVICEWIDTHPOINTS=288 -dDEVICEHEIGHTPOINTS=432 photo.ps -c quit